Figure 4
Glycosaminoglycans as Novel Targets for in vivo Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Atherosclerosis
Yavuz O Uca* and Matthias Taupitz
Published: 20 April, 2020 | Volume 5 - Issue 1 | Pages: 080-088
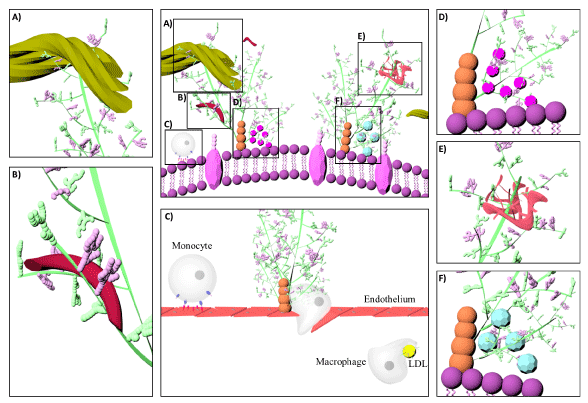
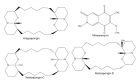
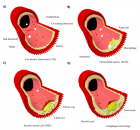
Figure 4:
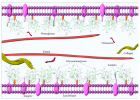
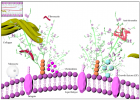
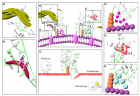
Schematic illustration of different glycosaminoglycan interactions. Glycosaminoglycans localize, stabilize, activate or inactivate proteins [98]. Decorin is a proteoglycan form of dermatan sulfate, which binds to collagen (A). Heparin interacts with fibronectin (B) [133]. Monocyte transmigration happen through interactions with the cell surface heparan sulfates on the endothelium and glycosaminoglycan low density lipoprotein complexes are more easily internalized by macrophages than lipoproteins alone (C) [101,127]. Glycosaminoglycans serve as storage reservoir for chemokines (D) and growth factors (F) [128]. They perform the highest affinity binding by inducing conformational changes and surface complementarity on the proteins [111,112]. Heparan sulfate-fibroblast growth factor and heparin anti thrombin III are the most well-known examples for such interactions (E).
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001091 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
More Images
Similar Articles
-
Left Atrial Remodeling is Associated with Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Reperfused Acute Myocardial InfarctionChristodoulos E. Papadopoulos*,Dimitrios G. Zioutas,Panagiotis Charalambidis,Aristi Boulbou,Konstantinos Triantafyllou,Konstantinos Baltoumas,Haralambos I. Karvounis,Vassilios Vassilikos. Left Atrial Remodeling is Associated with Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Reperfused Acute Myocardial Infarction. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001001; 1: 001-008
-
Mid-Ventricular Ballooning in Atherosclerotic and Non-Atherosclerotic Abnormalities of the Left Anterior Descending Coronary ArteryStefan Peters*. Mid-Ventricular Ballooning in Atherosclerotic and Non-Atherosclerotic Abnormalities of the Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001002; 1:
-
Concentration Polarization of Ox-LDL and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Human Endothelial CellsShijie Liu*,Jawahar L Mehta,Yubo Fan,Xiaoyan Deng,Zufeng Ding*. Concentration Polarization of Ox-LDL and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Human Endothelial Cells. . 2016 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001003; 1:
-
Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block: What is the Mechanism?Hussam Ali*,Riccardo Cappato. Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block: What is the Mechanism?. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001004; 2:
-
Congenital Quadricuspid Aortic Valve, a Rare Cause of Aortic Insufficiency in Adults: Case ReportCyrus Kocherla*,Kalgi Modi. Congenital Quadricuspid Aortic Valve, a Rare Cause of Aortic Insufficiency in Adults: Case Report. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001005; 2: 003-007
-
Short and Medium-Term Evaluation of Patients in Coronary Post-Angioplasty: Préliminary results at the Cardiology Department of the Hospital University Aristide Le Dantec of Dakar (Senegal): Study on 38 CasesDioum M*,Aw F,Masmoudi K,Gaye ND,Sarr SA,Ndao SCT, Mingou J,Ngaidé AA,Diack B,Bodian M,Ndiaye MB,Diao M,Ba SA. Short and Medium-Term Evaluation of Patients in Coronary Post-Angioplasty: Préliminary results at the Cardiology Department of the Hospital University Aristide Le Dantec of Dakar (Senegal): Study on 38 Cases. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001006; 2: 008-012
-
Indications and Results of Coronarography in Senegalese Diabetic Patients: About 45 CasesNdao SCT*,Gaye ND,Dioum M,Ngaide AA,Mingou JS,Ndiaye MB, Diao M,Ba SA. Indications and Results of Coronarography in Senegalese Diabetic Patients: About 45 Cases. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001007; 2: 013-019
-
Procedure utilization, latency and mortality: Weekend versus Weekday admission for Myocardial InfarctionNader Makki,David M Kline,Arun Kanmanthareddy,Hansie Mathelier,Satya Shreenivas,Scott M Lilly*. Procedure utilization, latency and mortality: Weekend versus Weekday admission for Myocardial Infarction. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001008; 2: 020-025
-
Spontaneous rupture of a giant Coronary Artery Aneurysm after acute Myocardial InfarctionOğuzhan Çelik,Mucahit Yetim,Tolga Doğan,Lütfü Bekar,Macit Kalçık*,Yusuf Karavelioğlu. Spontaneous rupture of a giant Coronary Artery Aneurysm after acute Myocardial Infarction. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001009; 2: 026-028
-
Thrombolysis, the only Optimally Rapid Reperfusion TreatmentVictor Gurewich*. Thrombolysis, the only Optimally Rapid Reperfusion Treatment. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jccm.1001010; 2: 029-034
Recently Viewed
-
Time Electron TheorySyed Munim Qadri*. Time Electron Theory. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001081; 7: 026-039
-
Approximation of Kantorovich-type Generalization of (p,q) - Bernstein type Rational Functions Via Statistical ConvergenceHayatem Hamal*. Approximation of Kantorovich-type Generalization of (p,q) - Bernstein type Rational Functions Via Statistical Convergence. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001080; 7: 019-025
-
Factors Influencing Knowledge on the Completion of Treatment among Tuberculosis Patients under Directly Observed Treatment Strategy (DOTS) in a Selected Health Facility, the BahamasEsther S Daniel*, Latasha Collie, Alice Neymour, Nicole KA Martin-Chen, Kevin Moss, Kathy-Ann Lootawan, Virginia M Victor. Factors Influencing Knowledge on the Completion of Treatment among Tuberculosis Patients under Directly Observed Treatment Strategy (DOTS) in a Selected Health Facility, the Bahamas. Clin J Nurs Care Pract. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001053; 8: 022-030
-
Individual Treatment Trial of PIGV-Associated Mabry Syndrome with D-Mannose in a Young ChildMarta Agnes Somorai*, Annabelle Arlt, Peter Krawitz, Jochen Baumkötter, Volker Mall. Individual Treatment Trial of PIGV-Associated Mabry Syndrome with D-Mannose in a Young Child. J Genet Med Gene Ther. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jgmgt.1001008; 6: 001-004
-
Biomarkers for High Metabolic Burden in Neurologic DiseaseVictor B Stolberg*. Biomarkers for High Metabolic Burden in Neurologic Disease. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001091; 8: 012-013
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."