About The University of Manchester
The University of Manchester
Articles by The University of Manchester
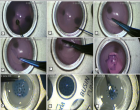
Femoral venous closure: A single-centre retrospective analysis in real world all comers with MynxGrip® vascular closure device
Published on: 18th June, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8628667812
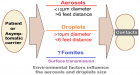
Background: Vascular closure devices (VCD) are routinely used to achieve haemostasis following percutaneous arterial procedures. The extravascular polyethylene-glycol based MynxGrip® device (Cardinal Health) received FDA approval for use in the closure of femoral veins, but so far limited data is available on its use, especially with concomitant use of anticoagulants.
Method: This is a retrospective analysis of data from a single-centre on the effectiveness and complication rates following the use of the MynxGrip® device for femoral venous closure in patients undergoing diagnostic/interventional (temporary pacing during balloon aortic valvuloplasty, or electrophysiology) procedures utilising 5-7F sheaths.
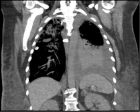
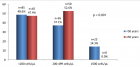
Results: 85 patients (mean age 74 years) underwent femoral venous closure with the MynxGrip® device. 51.8% were male. The rate of concomitant anticoagulant or antiplatelet use was 52.9%. Device deployment was 100% successful with full haemostasis in all cases. There were no major vascular complications (bleeding, thrombosis, or infections). There was one case of a minor small venous hematoma which did not require treatment. The mean length of stay was less than 1 day (67.1% patients discharged the same day) and overnight stay only indicated by interventional procedure.
Conclusion: These data support safety and efficacy of the MynxGrip® device for femoral venous closure with same-day discharge, even with concomitant aggressive antiplatelet and anticoagulant use. It has the potential for use in other large bore venous access sites.
Step VEP visual acuity in a pediatric neuro-ophthalmological cohort
Published on: 12th June, 2022
Steady-state VEPs, have been used to estimate visual acuity since the 1970s and allow responses to a range of stimulus sizes to be collected rapidly- with particular utility in infants. However, the assessment of children with cortical visual impairment is a bigger challenge that lead to the development of the Step VEP. Its initial evaluation revealed that accuracy and precision were poorer for pediatric patients than for optically degraded normal adults and that it was not necessarily successful in every child. Statistical models generated the equations: VAO = 0.56 VAStep (r2 = 0.75, F = 60.93, p = 0.000) and VAPL = 0.45 VAStep (r2 = 0.82, F = 156.85, p = 0.000), supported by a recent a systematic review of VA comparisons showing that recognition VA (optotypes) agrees more closely than discrimination VA (PL) with VEP VA. In combination, Step VEPS and subjective tests allowed complete assessment in 96% of patients, with incomplete Step VEPS much more likely to be partially successful than not, and more likely to be partially successful than incomplete subjective tests. This supports the rationale that Step VEPs maintain attention by limiting the time spent stimulating away from an individual’s threshold of spatial resolution. For the small number of patients in whom VA cannot be estimated, alternative stimuli and methods of presentation are proposed.
VEP visual acuity in children with cortical visual impairment
Published on: 2nd August, 2022
Given improvements in neonatal care and the increased survival rates of infants born pre-term, Cortical Visual Impairment (CVI) is now the leading cause of visual impairment (VI) in the developed world. In this study, Step VEPS, transient VEPS and Vernier Sweep VEPs all demonstrated unbiased relationships with Preferential looking (PL) cards over the whole range of Visual Acuity (VA) in children with CVI, allowing equations for clinical use to be derived. The results also suggested that a slower, vernier steady-state stimulus of 80% contrast and presented with the Step VEP algorithm could further improve VA agreement with PL and optimise developmental sensitivity. An eye tracking device has proved very useful in the clinical assessment of this cohort. It is also now known that children can have good VA and CVI, and that sweep VEPS can highlight higher processing deficits. As well as negative findings, compensatory neuroplasticity is thought to occur during maturation and it is now realistic to study this mechanism, and other age-related changes across VI with functional tests and neuroimaging (including VEPS). A cross-sectional study of adults would highlight CVI’s ultimate functional limitations.

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."